
Artificial intelligence business acquisitions are evolving rapidly, offering exciting new opportunities alongside significant hidden risks that demand careful navigation. In 2024, global AI business investment surged impressively, with private funding in U.S.-based AI companies alone exceeding $109 billion, and worldwide investment across sectors reaching well over $140 billion. This level of investment reflects the growing confidence in AI business potential across industries such as healthcare, finance, and manufacturing.
However, this rapid growth also brings unique challenges. AI businesses command median revenue multiples around 29.7 times—substantially higher than the typical 6.7 times multiples seen in traditional software firms. These inflated valuations can obscure significant underlying risks, from technical complexities to scaling challenges, that conventional due diligence often fails to uncover. Successful buyers are those who recognize and rigorously evaluate these hidden factors long before signing purchase agreements, safeguarding value and positioning themselves for sustainable growth in this dynamic market.
The AI Acquisition Landscape in 2025
Market Size and Growth Projections
The global AI market generated $95 billion in total funding across 5,084 deals in 2024. This represents a 10% increase from the previous year’s record investment levels. Enterprise adoption of AI solutions accelerated following ChatGPT’s breakthrough in late 2022.
Investment rounds in the AI space increased nearly 4x over the past decade. Early-stage funding dominated the landscape with 32% of all deals occurring at seed stage. This concentration indicates the AI ecosystem remains in its formative development phase.
Revenue projections for leading AI companies reach astronomical levels. Anthropic expects to generate $12 billion by 2027 from its current minimal revenue base. These projections drive investor excitement and inflated business valuations.
Why Investors Are Flocking to AI Businesses
Investors are flocking to AI businesses for these reasons:
- AI businesses create competitive advantages through proprietary algorithms and exclusive data networks, enabling continuous improvement and unique network effects.
- Switching costs for AI solutions exceed those of conventional software because companies integrate AI deeply into operational workflows, creating stronger customer retention.
- Market demand for AI spans every industry sector—including healthcare, finance, cybersecurity, and manufacturing—driving broad investor confidence in long-term growth potential.
The Hidden Complexity Behind AI Success Stories
AI startups operate in research-intensive environments that require substantial ongoing investment. Companies must continuously train models and retain specialized talent. These operational demands create cash flow challenges that acquisition analysis often overlooks.
Revenue recognition in AI businesses differs significantly from traditional software models. Many companies generate income through data licensing rather than recurring subscriptions. This creates revenue volatility that impacts long-term business stability.
Technology obsolescence threatens AI businesses more rapidly than conventional software companies. New breakthroughs can render existing solutions worthless overnight. This innovation risk demands careful evaluation during acquisition processes.
Valuation Nightmares – When Numbers Don’t Add Up
Beyond Traditional Metrics – The AI Valuation Puzzle
Traditional valuation methods fail to capture AI business complexity accurately. Revenue multiples ignore critical factors like algorithm performance and data quality. Due diligence teams must evaluate technical capabilities beyond financial statements.
Algorithm accuracy determines long-term business viability more than current revenue figures. AI models with superior performance command premium pricing and customer retention. Buyers must validate these technical claims through independent testing procedures.
Data ownership represents the most valuable asset in many AI acquisitions. Companies with proprietary datasets maintain sustainable competitive advantages. However, data licensing agreements can create hidden liabilities that impact future profitability.
| Valuation Factor | Traditional Software | AI Business | Impact Level |
| Revenue Multiple | 6.7x | 29.7x | Critical |
| Data Assets | Low | High | Critical |
| Algorithm Performance | N/A | Critical | High |
| Technical Team | Medium | Critical | High |
| Infrastructure Costs | Low | High | Medium |
The Multiples Trap – Understanding Real vs. Inflated Values
Capital raising transactions generate higher multiples than actual acquisition deals. Public funding rounds create artificial price benchmarks that mislead acquisition valuations. Smart buyers distinguish between investment hype and realistic purchase prices.
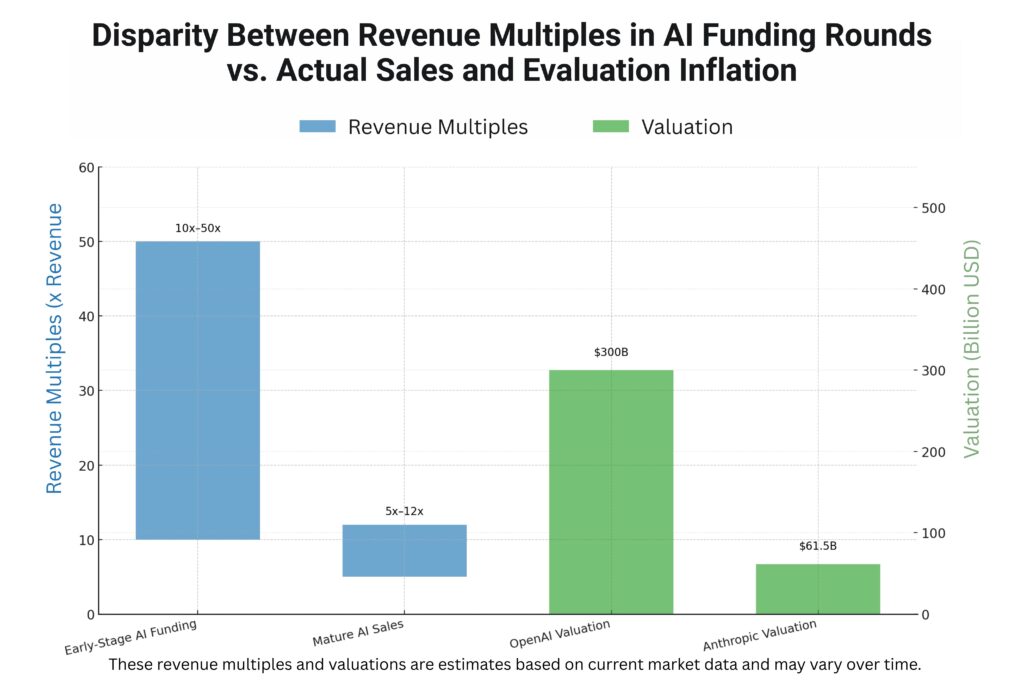
Early-stage AI companies trade at 10x-50x revenue multiples during funding rounds. Mature AI businesses command more reasonable 5x-12x multiples in actual sales. This disparity creates expectation gaps between sellers and realistic buyers.
OpenAI discussions valued the company at $300 billion despite limited revenue transparency. Anthropic projections suggest a $60 billion valuation based on future revenue estimates. These examples demonstrate the valuation inflation affecting AI business sales.
Hidden Costs That Destroy ROI
Infrastructure expenses for AI businesses exceed traditional software operational costs significantly. Companies require substantial computing power for model training and inference. These ongoing costs continue indefinitely and impact acquisition returns.
Talent retention costs in AI businesses often double post-acquisition budgets. Specialized AI engineers command premium salaries that increase annually. Key person dependencies create additional retention risks that affect business continuity.
Compliance costs for AI businesses grow rapidly as regulatory frameworks evolve. Companies must invest in bias testing, model explainability, and data privacy measures. These requirements create unexpected operational expenses that reduce profit margins.
Technical Due Diligence Pitfalls
Algorithm Performance vs. Marketing Claims
Marketing materials from AI companies often exaggerate actual technical capabilities. Sellers highlight best-case performance scenarios while hiding model limitations. Buyers must conduct independent technical assessments to verify algorithm effectiveness.
Benchmark testing reveals the true performance of AI systems under realistic conditions. Many companies optimize models for specific test cases that don’t represent real-world usage. Performance degradation occurs when systems handle diverse production data.
Third-party validation provides objective assessment of AI capabilities beyond seller claims. Independent technical experts can identify algorithmic weaknesses that internal teams might overlook. This validation prevents costly acquisition mistakes.
Data Dependencies and Ownership Issues
Data quality determines AI system effectiveness more than algorithm sophistication. Poor quality training data produces unreliable model outputs regardless of technical architecture. Data assessment requires specialized expertise to evaluate properly.
Third-party data dependencies create ongoing licensing risks and operational vulnerabilities. Companies relying on external data sources face supply chain disruptions that affect system performance. Buyers must understand these dependencies before finalizing acquisitions.
Data portability challenges arise when acquired companies use proprietary formats or specialized storage systems. Migration costs and technical complexity can exceed initial acquisition budgets significantly. These challenges require careful evaluation during due diligence.
Scalability Myths and Infrastructure Reality
Scalability claims from AI companies often ignore infrastructure requirements and associated costs. Systems that work effectively at small scale may fail when processing enterprise-level data volumes. Load testing reveals these limitations before acquisition completion.
Computing resources for AI systems scale non-linearly with usage increases. Infrastructure costs can grow exponentially rather than proportionally with business expansion. This creates margin pressure that acquisition models rarely anticipate accurately.
Integration challenges with existing systems create additional technical complexity and expense. AI solutions often require custom APIs and specialized data pipelines. These integration requirements extend implementation timelines and increase project costs.
Regulatory and Compliance Landmines
The Shifting AI Regulatory Environment
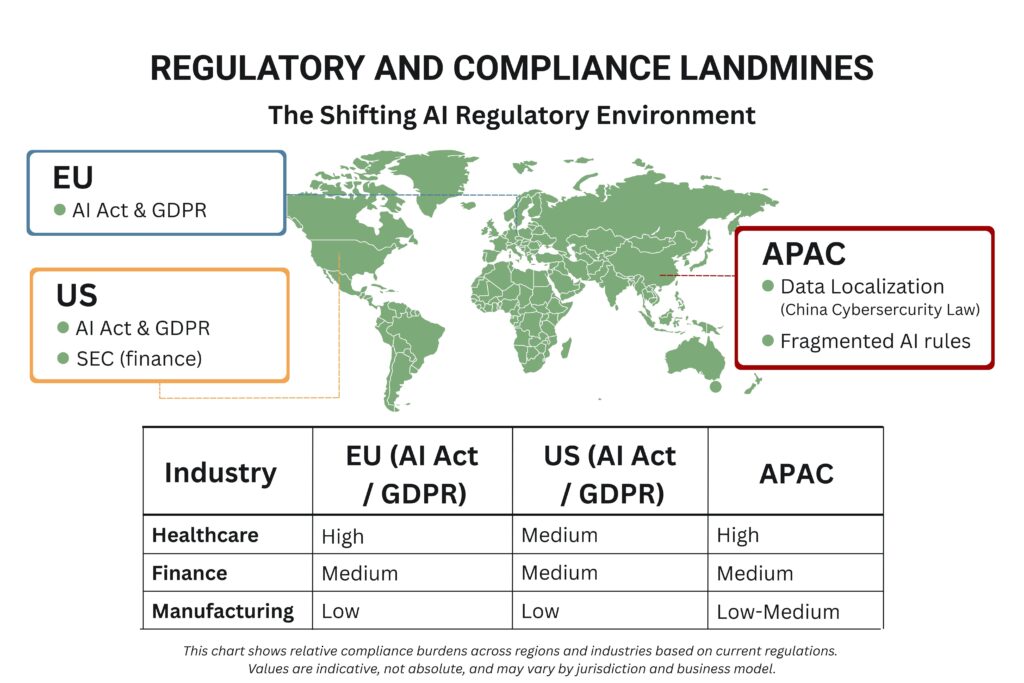
Regulatory frameworks for AI businesses evolve rapidly across global jurisdictions. The European Union’s AI Act creates comprehensive compliance requirements for AI systems. Regulatory compliance costs continue indefinitely and affect operational margins.
Industry-specific regulations add additional complexity for AI businesses serving regulated sectors. Healthcare AI companies must comply with HIPAA requirements and FDA approval processes. Financial AI solutions face SEC oversight and banking regulations.
Cross-border operations create multiple regulatory compliance obligations that vary by jurisdiction. Companies operating globally must navigate conflicting requirements across different regulatory systems. This complexity increases legal costs and operational risks.
Ethics and Bias – The Invisible Liability
Algorithm bias creates significant legal and reputational risks for AI businesses. Discriminatory outcomes from AI systems can trigger class action lawsuits and regulatory penalties. These risks often remain hidden until post-acquisition operations.
Explainability requirements force AI companies to document and justify algorithmic decisions. Transparency obligations increase development costs and limit certain AI techniques. Companies must balance performance optimization with regulatory compliance.
Ethical AI practices require ongoing monitoring and adjustment of algorithmic systems. Bias detection tools and fairness metrics add operational complexity and expense. These requirements continue throughout the business lifecycle.
Data Privacy and Security Compliance Costs
GDPR compliance affects any AI business processing European customer data. Privacy requirements include data minimization, consent management, and deletion capabilities. Non-compliance penalties reach 4% of global annual revenue.
Data localization requirements in various countries restrict AI system architecture and deployment options. Residency obligations increase infrastructure costs and operational complexity significantly. These requirements limit market expansion opportunities.
Security standards for AI systems exceed traditional software protection requirements. Data breaches involving AI training data create amplified liability and regulatory exposure. Companies must invest heavily in cybersecurity measures to protect valuable data assets.
Talent and Knowledge Transfer Challenges
The AI Talent Retention Crisis
AI specialists command premium salaries that increase 15-20% annually across the industry. Talent competition from tech giants creates retention challenges for acquired companies. Key employees often leave post-acquisition, taking critical knowledge with them.
Stock option packages for AI talent often exceed acquisition budgets for retention programs. Golden handcuffs become necessary to prevent mass exodus of technical teams. These retention costs can double initial acquisition valuations.
Recruitment costs for replacement AI talent reach $150,000-$300,000 per senior position. Time-to-productivity for new AI engineers extends 6-12 months due to system complexity. These factors create significant business continuity risks during transitions.
Knowledge Transfer and Documentation Gaps in AI Acquisitions
When AI companies are acquired, effective knowledge transfer and documentation are crucial to maintain capabilities and ensure smooth integration. This list highlights the main challenges buyers face due to gaps in documentation, standardized processes, and specialized training needs:
- Technical documentation often lives primarily in developers’ minds rather than formalized systems, making knowledge transfer during acquisition critical to avoid capability loss.
- AI model development processes frequently lack formal standards, concentrating knowledge in key individuals who may leave post-acquisition, creating risks to business continuity.
- Specialized expertise is required to train AI systems, and onboarding new technical staff is more complex than in traditional software environments, extending integration timelines and raising costs.
Cultural Integration in Research-Heavy Environments
Academic culture in AI research teams often conflicts with commercial operational requirements. Innovation priorities may not align with business objectives and revenue generation. This cultural mismatch creates management challenges during integration periods.
Research timelines in AI development extend beyond typical business planning horizons. Long-term projects may not generate revenue for years after acquisition completion. Buyers must balance innovation investment with immediate return expectations.
Publication practices common in AI research can conflict with intellectual property protection strategies. Academic teams may resist proprietary development approaches that limit knowledge sharing. This creates competitive protection challenges for commercial operations.
Strategic Integration and ROI Realization Risks
Technology Integration Complexities
API compatibility between acquired AI systems and existing infrastructure creates significant technical challenges. Legacy systems often lack the computational capacity to support AI workloads effectively. Integration projects frequently exceed initial timeline and budget estimates.
Data pipeline integration requires specialized expertise and substantial development resources. Format conversions and schema mapping add complexity that traditional software acquisitions don’t face. These technical requirements create implementation delays and cost overruns.
System architecture differences between AI and traditional software create modernization requirements for existing infrastructure. Cloud migration and scalability improvements become necessary for AI system deployment. These upgrade costs often surprise acquisition teams.
Market Positioning and Competitive Threats
Technology obsolescence threatens AI businesses more rapidly than conventional software companies. Breakthrough announcements from competitors can render existing solutions obsolete within months. This innovation risk requires continuous R&D investment to maintain competitiveness.
Tech giants like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon compete directly with acquired AI companies using virtually unlimited resources. Platform competition creates margin pressure and limits growth opportunities for smaller players. David versus Goliath dynamics favor established players.
Market timing affects AI business success more dramatically than traditional software acquisitions. Early adoption phases offer higher margins but carry execution risks. Mature markets provide stability but reduce growth potential and acquisition premiums.
ROI Timeline Reality Check
Payback periods for AI acquisitions extend 3-5 years longer than traditional software deals. Revenue ramp occurs more slowly due to enterprise sales cycles and integration complexity. Patient capital becomes essential for value realization.
Ongoing investment requirements for AI businesses continue indefinitely to maintain competitive positions. Model retraining, infrastructure scaling, and talent retention create perpetual cash requirements. These costs reduce net returns below initial projections.
Market maturation affects AI business growth trajectories as competition increases and price compression occurs. First-mover advantages erode over time, reducing premium pricing power and acquisition multiples. Buyers must model these dynamics carefully.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the typical timeline for AI business due diligence?
Technical complexity extends standard due diligence processes from 30-60 days to 90-120 days for AI acquisitions. Algorithm assessment and data quality evaluation require specialized expertise that traditional teams lack. Regulatory compliance review adds additional time requirements.
How do AI business valuations compare to traditional software companies?
AI companies command median revenue multiples of 29.7x compared to 6.7x for traditional software businesses. However, hidden costs and ongoing investment requirements often offset these premium valuations. Risk-adjusted returns may favor traditional software acquisitions.
What are the biggest red flags to watch for in AI business acquisitions?
Over-reliance on third-party data sources creates supply chain vulnerabilities and licensing risks. Unproven scalability claims without supporting infrastructure demonstrate execution risks. Regulatory non-compliance or lack of bias testing creates legal liability exposure.
Should I hire specialized consultants for AI business due diligence?
Technical AI expertise is critical for proper evaluation of algorithm performance and data assets. Regulatory specialists help identify compliance risks that general legal teams might miss. Specialized consultants prevent costly mistakes that exceed their fees significantly.
What’s the failure rate for AI business acquisitions?
AI acquisitions show higher failure rates than traditional technology M&A due to complexity factors and valuation challenges. Integration difficulties and talent retention issues contribute to underperformance compared to initial projections. Proper due diligence reduces these risks substantially.
Smart Acquisition Strategies for 2025
Successful AI acquisitions require specialized expertise and extended due diligence timelines. Technical assessment teams must include AI specialists who understand algorithmic performance and data quality. Legal teams need regulatory expertise specific to AI compliance requirements.
Valuation models for AI businesses must account for hidden costs and ongoing investment requirements. Financial projections should model worst-case scenarios for talent retention and regulatory compliance. Conservative assumptions prevent overpayment and improve acquisition returns.
Integration planning must begin during due diligence to identify technical compatibility issues and cultural challenges. Risk mitigation strategies require specific expertise in AI operations and regulatory compliance. Proper planning prevents post-acquisition surprises. Ready to navigate the complex world of AI business acquisitions? The experts at Bookman Capital have guided dozens of successful acquisitions of AI companies. Get your free consultation and acquisition strategy assessment today. Contact Bookman Capital at bookmancapital.io to ensure your next AI acquisition delivers the returns you expect.
Sources:
